Peking University November 1, 2022: The
Journal of the American Chemical Society recently published an article online entitled “Mechano-bioconjugation Strategy Empowering Fusion Protein Therapeutics with Aggregation Resistance, Prolonged Circulation, and Enhanced Antitumor Efficacy,” written by Zhang Wenbin’s research group from the PKU College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering. They reported using mechano-bioconjugation as a novel approach to empower fusion protein therapeutics and demonstrated its utility by a protein heterocatenane (cat-IFN-ABD) containing interferon-α2b (IFN) mechanically interlocked with a consensus albumin-binding domain (ABD). Their path-breaking insights provide an alternative pathway for developing advanced protein therapeutics.
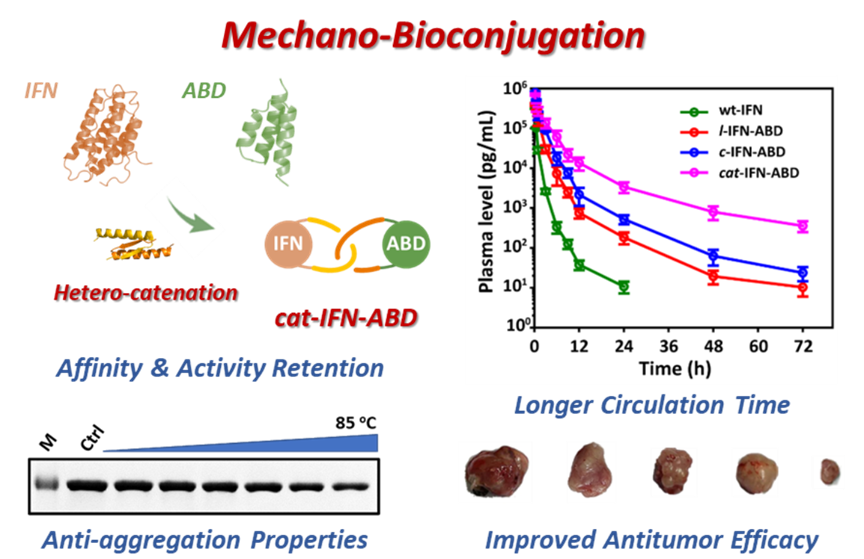
Bioconjugation is a powerful protein modification strategy to improve protein properties. Zhang Wenbin’s research group has found that the conjugate was selectively synthesized in cellulo following a cascade of post-translational events using a pair of heterodimerizing p53dim variants and two orthogonal split-intein reactions. The catenane topology was proven by combined techniques of LC–MS, SDS-PAGE, SEC, and controlled proteolytic digestion. According to Zhang Wenbin’s group, not only did cat-IFN-ABD retain activities comparable to those of the wild-type IFN and ABD, the conjugate also exhibited enhanced aggregation resistance and prolonged circulation time over the simple linear and cyclic fusions. Consequently, cat-IFN-ABD potently inhibited tumor growth in the mouse xenograft model.
The J
ournal of the American Chemical Society publication of Zhang Wenbin’s group (
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/jacs.2c06532) was promptly followed by the recommendation and evaluation of Faculty Opinions (
https://facultyopinions.com/article/742344893). Liu Yajie, Ph.D. of College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Peking University, is the first author of this paper. Zhang Wenbin, and Wei Wei, from Institutes of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences are co-corresponding authors of this paper. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, National Key Research and Development Program of China, Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Clinical Medicine Plus X-Young Scholars Project of Peking University, Open Funding Project of the State Key Laboratory of Biochemistry Engineering and the Doctoral Scientific Research Fund of Ministry of Education of China.
Congratulations to the team on their groundbreaking research!
Written by: Feng Liyuan
Edited by: Ng Joong Hwee
Source: PKU News (
Chinese)